for IoT and M2M Applications
Executive summary
Single twisted pair ethernet cabling traces its roots back to the late 19th century, when Alexander Graham Bell introduced this technology as a way to transmit voice traffic while overcoming interference.
Today, twisted-pair copper continues to play a crucial role in communications. Significantly improved from the first telephone wire that carried Bell’s voice, twisted-pair is prevalent in Ethernet networks, supporting commonly available equipment with data rates up to 10 Gbps. Meanwhile, engineers have been able to tap the ability of balanced twisted-pair to deliver dc power, as well as data, over the same cable.
Advancements in twisted-pair cabling coincide with a growing realization that the best cabling solution is the one that most effectively meets all application requirements. Faster is not necessarily better. One need only look at the increasing deployment of the Internet of Things (IoT) to understand the significance of this shift and the opportunities it is creating.
“Today, the desire to bring the advantages of Ethernet into new applications necessitates a new approach where the needs of the application are considered first and foremost in defining new Ethernet incarnations.”
—David Chalupsky, director, Ethernet Alliance Board of Directors
In the coming years, enterprise IT professionals will be charged with integrating a wide assortment of connected devices into their structured cabling networks. Some will require the power output and/or high-bandwidth capacity only four-pair Ethernet cabling can support. But, for devices with minimal power and bandwidth requirements—such as sensors and actuators used for building automation and manufacturing equipment, alarm systems and RFID readers—the use of single-pair Ethernet cabling can provide a more cost-effective and space-efficient solution.
To efficiently support these applications, the industry is beginning to explore the possibilities for single-pair Ethernet. Standards bodies have ramped up efforts to develop guidelines for a variety of applications Single Twisted Pair Ethernet Cabling for IoT and M2M Applications
involving single balanced twisted-pair as well as the components used in its deployment. Application specifications have been published
or are under development in IEEE 802.3. These include 802.3bp 1000BASE-T1, 802.3bw 100BASE-T1, 802.3bu PoDL (0.5 watt to 50 watts) and 802.3cg 10 Mbps Ethernet.
While it is not meant to replace traditional four-pair Ethernet cabling, the business use case for single-pair Ethernet is emerging. When used in support of appropriate applications, single-pair Ethernet provides significant advantages.
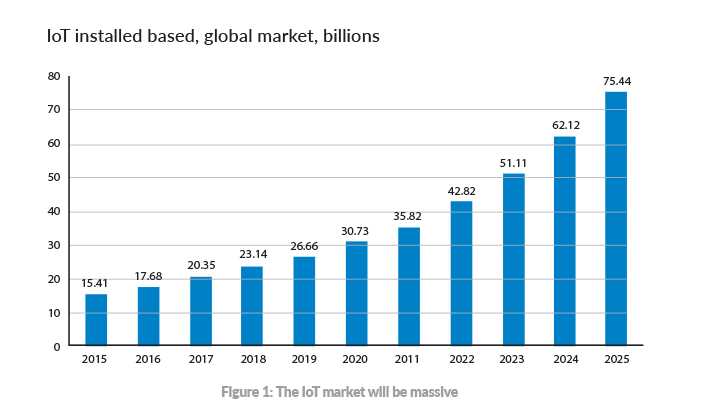
IoT applications are opening the door for single-pair Ethernet By 2018, IoT-based sensors and devices are expected to exceed mobile phones as the largest category of connected devices.1 By 2020, estimates predict there will be about 200 billion connected objects worldwide2 —or 26 devices for every person on Earth.
While consumer-based applications—think wearables, home automation and automotive telematics—attract much of the general media attention, they pale in comparison to the industrial IoT (IIoT). By 2025, the total global worth of IoT technology could be as much as USD 6.2 trillion, with USD 4.8 trillion coming from health care (USD 2.5 trillion) and manufacturing (USD 2.3 trillion) alone.3 Most of the growth will come from machine-to-machine (M2M) connections needed to drive manufacturing, distribution, agriculture, industrial processing, healthcare and other professional services.
Single Twisted Pair Ethernet Cabling for IoT and M2M Applications
Enterprise IT teams are just now beginning to wrestle with how to connect the various sensors, controls, cameras and…..
